Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a vital fat-soluble nutrient crucial for vision, immune function, and skin health. It occurs in two forms: retinoids from animal sources and carotenoids from plants. Adequate intake supports overall health, particularly eye health and immune system strength. Balancing dietary sources ensures optimal well-being.
About Vitamin A
Our comprehensive guide to Vitamin A explores this vital nutrient essential for overall health and well-being. Vitamin A is a fat-soluble compound known for its pivotal role in various bodily functions, making it a crucial component of a balanced diet.
This essential vitamin comes in two primary forms: retinoids and carotenoids. Retinoids, found in animal-based foods such as liver, dairy products, and fish, are readily converted into active forms of Vitamin A in the body. On the other hand, carotenoids are found in colorful fruits and vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach. These plant-based sources provide provitamin A carotenoids, which your body can convert into Vitamin A.
Vitamin A plays a multifaceted role in maintaining optimal health. It is well-known for supporting healthy vision, especially in low-light conditions, and is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system. Additionally, it promotes skin health, cell growth, and reproductive function.
Health Benefits of Vitamin A
Healthy Vision
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining good eyesight, particularly in low-light conditions. It helps prevent night blindness and supports the proper functioning of the retina.
Immune System Support
Vitamin A plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses. It enhances the production of white blood cells and antibodies.
Skin Health
This vitamin promotes healthy skin by supporting cell growth and repair. It’s often used in skincare products to reduce signs of aging and improve skin texture.
Reproductive Health
Vitamin A is important for both male and female reproductive health. It plays a role in the development of sperm, and in females, it is essential for a healthy pregnancy and fetal development.
Bone Health
It contributes to bone health by promoting the synthesis of proteins necessary for bone formation.
Cell Growth and Development
Vitamin A is involved in the growth and development of cells, including those in the heart, lungs, and kidneys.
Antioxidant Properties
Some forms of Vitamin A act as antioxidants, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which can reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Healthy Teeth and Gums
It supports oral health by promoting the health of the mucous membranes and tissues in the mouth.
Cancer Prevention
Adequate Vitamin A intake may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as lung and prostate cancer, due to its antioxidant properties.
Skin Disorders
Vitamin A derivatives (retinoids) are used in the treatment of skin conditions like acne and psoriasis.
Perils of Deficient Vitamin A Intake
Night Blindness
One of the early signs of Vitamin A deficiency is night blindness, which makes it difficult to see in low-light conditions. This condition can impair a person’s ability to drive or perform tasks in dimly lit environments.
Xerophthalmia
In severe cases, VAD can progress to xerophthalmia, a condition that causes the cornea to become dry and thickened. If left untreated, it can lead to irreversible blindness.
Weakened Immune System
Vitamin A is essential for a strong immune system. Deficiency can make individuals more susceptible to infections, including respiratory and gastrointestinal infections.
Delayed Growth and Development
Children with VAD may experience stunted growth and delayed development. It can affect their physical and cognitive development, leading to long-term consequences.
Increased Mortality Risk
Vitamin A deficiency is a significant public health concern in many parts of the world, particularly in developing countries. It is associated with a higher risk of mortality, especially among young children and pregnant women.
Skin Problems
VAD can result in dry, scaly skin, and an increased susceptibility to skin infections.
Reduced Reproductive Health
In women, Vitamin A deficiency can lead to complications during pregnancy, such as an increased risk of maternal mortality, premature birth, and low birth weight in infants.
Decreased Bone Health
Insufficient Vitamin A intake can negatively impact bone health, potentially leading to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
Impaired Cognitive Function
Inadequate Vitamin A levels may affect cognitive function and lead to learning difficulties in children.
Increased Vulnerability to Chronic Diseases
Some research suggests that VAD may be linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases, including certain types of cancer and cardiovascular conditions.

Sources of Vitamin A
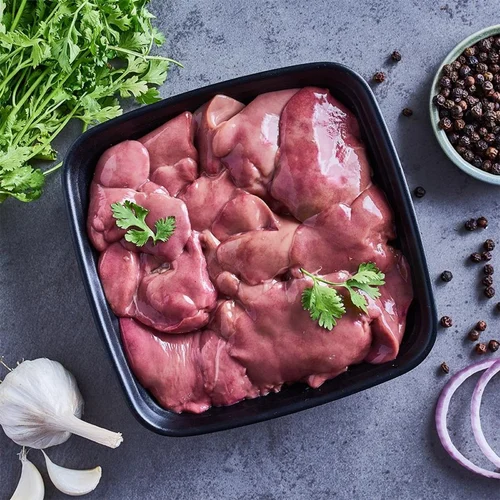
Animal-Based Foods: Preformed vitamin A is abundant in animal-based foods, especially in the form of retinol. Some of the best sources include
- Liver (beef, chicken, pork, and fish)
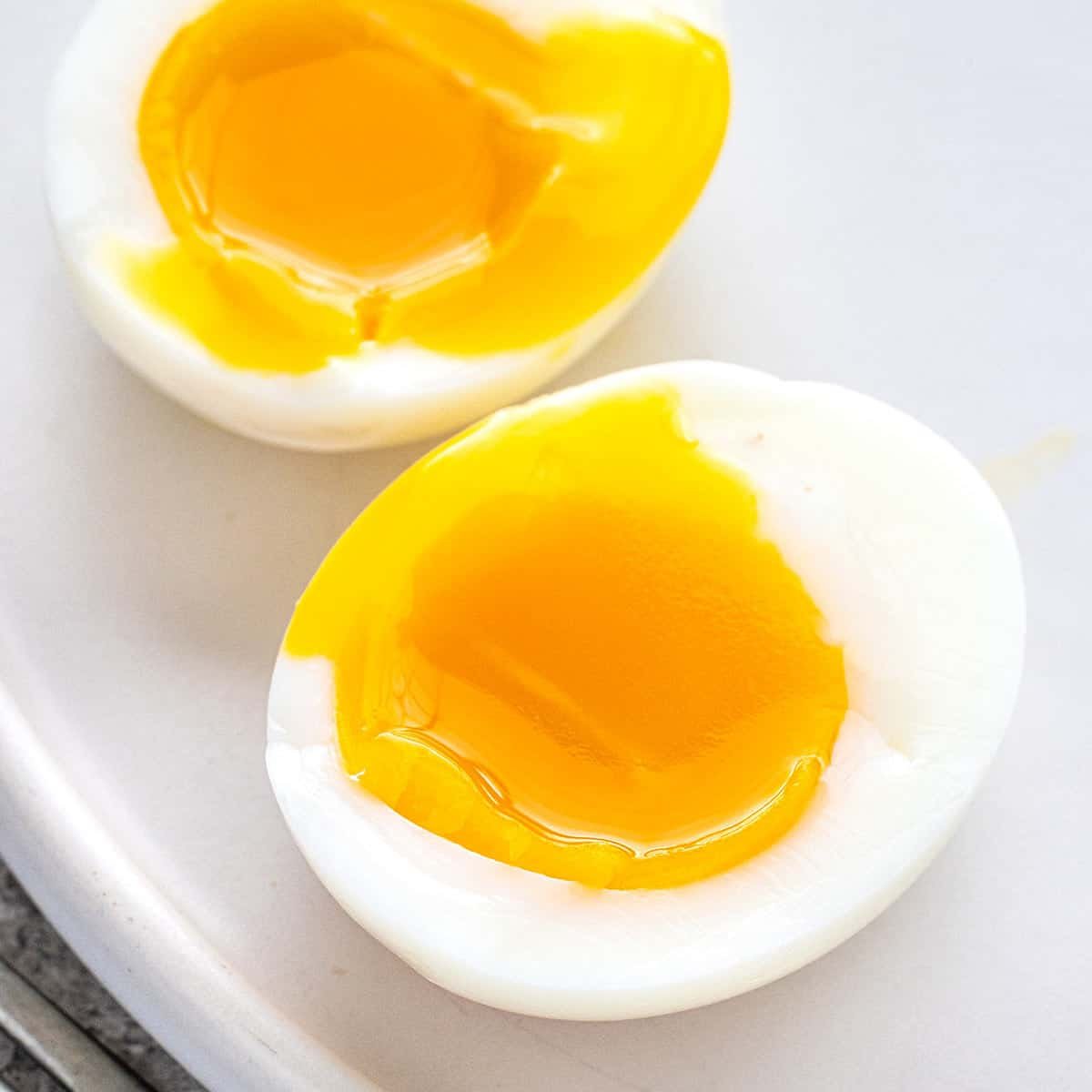
- Eggs
- Dairy Products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
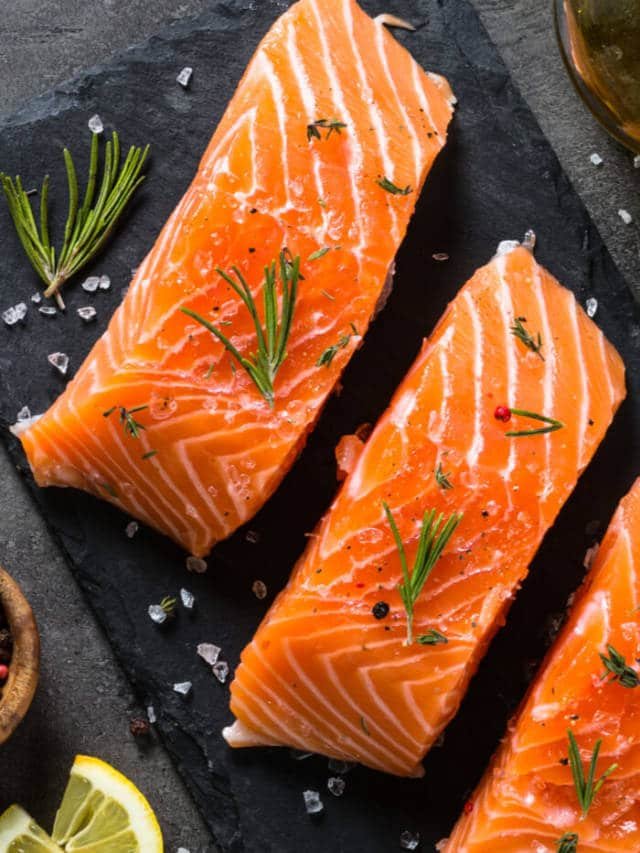
- Fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
Plant-Based Foods: Provitamin A carotenoids are found in plant-based foods and can be converted by the body into active vitamin A. The most well-known carotenoid is beta-carotene. Excellent sources include
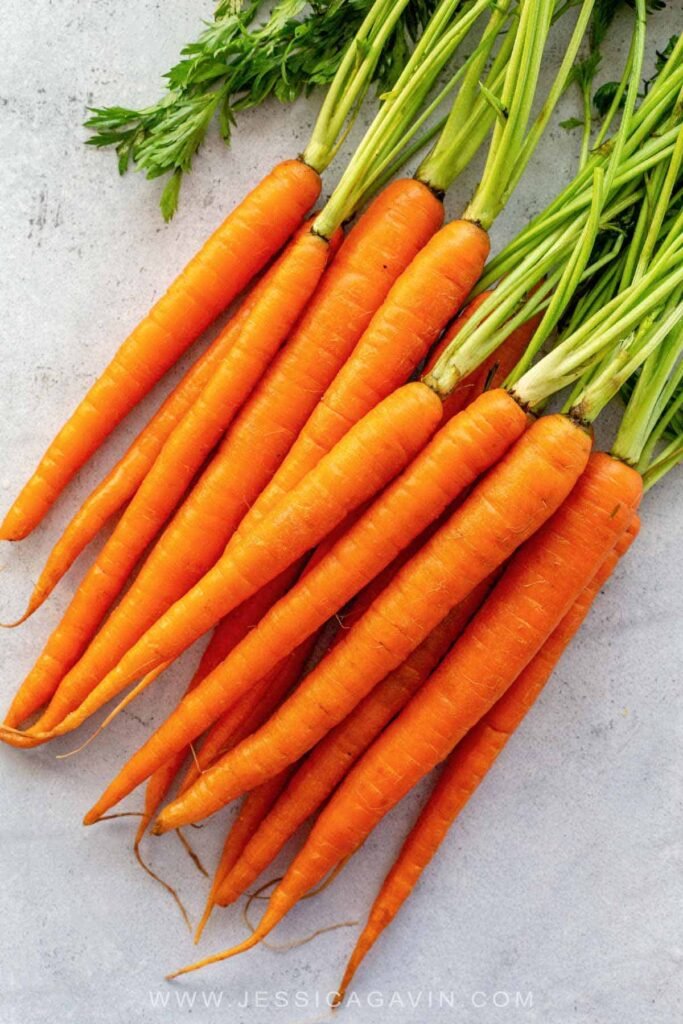
- Carrots
- Sweet Potatoes
- Butternut squash
- Spinach
- Kale
- Collard greens
- Red bell peppers
- Tomatoes
- Fruits like Mangoes, Papaya and Apricots





Frequently Asked Questions About Vitamin A
Welcome to our Vitamin A FAQs section, where we address common questions and provide you with accurate information to help you understand the importance of this essential nutrient.
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It’s essential for maintaining healthy vision, a robust immune system, and the proper functioning of vital organs like the heart and lungs.
Vitamin A exists in two main forms: preformed Vitamin A (retinoids), found in animal-based foods, and provitamin A carotenoids, found in plant-based foods. Both can be converted into active Vitamin A in the body.
Animal-based sources of Vitamin A include liver, dairy products, and fish. Plant-based sources rich in provitamin A carotenoids include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and kale.
Yes, Vitamin A deficiency can result in various health issues, including night blindness, weakened immunity, dry skin, and even more severe conditions in extreme cases. It’s vital to maintain adequate Vitamin A intake.
Yes, excessive Vitamin A intake, especially from supplements, can lead to toxicity, causing symptoms like nausea, dizziness, and, in severe cases, even organ damage. It’s crucial to follow recommended dietary guidelines.
Yes, Vitamin A plays a role in skin health. It supports skin cell production and repair and is commonly used in skincare products for its potential to improve skin texture and reduce signs of aging.
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision. It helps form light-sensitive pigments in the eyes, which are critical for low-light and color vision. A deficiency can lead to night blindness and other eye problems.
Yes, Vitamin A is known for its immune-boosting properties. It supports the integrity of mucosal surfaces, including those in the respiratory and digestive tracts, helping to defend against infections.
Vitamin A is essential during pregnancy for fetal development. However, excessive intake, especially in supplement form, can be harmful to the fetus. Pregnant women should follow their healthcare provider’s guidance.
Yes, interactions can occur. For example, certain medications, like cholesterol-lowering drugs, may reduce the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including Vitamin A. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about interactions.
Remember, while the information provided here offers general guidance, individual dietary needs and health conditions can vary. For personalized advice or concerns about your health, consult a healthcare professional.
Celebrate the Visionary Power of Vitamin A. From Bright Eyes to Strong Defenses, Vitamin A Empowers Your Health’s Advances.
